
Image credits: Penna Electric
Commercial buildings have different requirements for powering up their businesses in terms of lighting, HVAC, equipment, and technology. Electricity might have a backstage presence, but it is exactly what forms the “nervous system” for any building type. In the commercial world where on-and-off meet zeros-and-ones more than ever, electrical projects have a massive demand to support custom and lightning-fast solutions. Since electricity is a major expense, business owners plan various facility management techniques to lower their utility consumption and bring down the bills. For this reason, understanding the commercial electrical cost per square foot is a useful starting point if you are building or renovating your commercial space – and in this article, we discuss just that.
Commercial electrical cost per square foot
Electrical systems for a commercial building can differ based on the type of business you run and the operations that go on every day. On average, commercial electrical wiring can cost between $2 – $12 per square foot. The costs to wire a commercial building are generally higher than those for residential buildings because commercial spaces have heavy-duty power demands. So, for the same square footage, an office or a hospital will be costlier to power up compared to a residential home. The average range can go up or down depending on business-specific factors that we will see below.
Here is a good reference guide by Iota Communications for commercial electrical costs per square foot based on building types and utility needs. Lighting takes up a considerable portion of the electrical makeup – along with specialty operations that rely on commercial appliances and hospital equipment. Also, these specialty units tend to be more expensive than other electrical components in terms of both installation costs and energy consumption. As a result, restaurants and hospitals are ranked on the high end of this cost spectrum. Restaurants use large-scale refrigeration units and similar appliances that are quite power-hungry. Hospitals also rely on good ventilation in addition to medical machines that are expected to run 24/7. For both of these reasons, such commercial spaces incur higher electrical setup and maintenance costs per square foot compared to other building types.
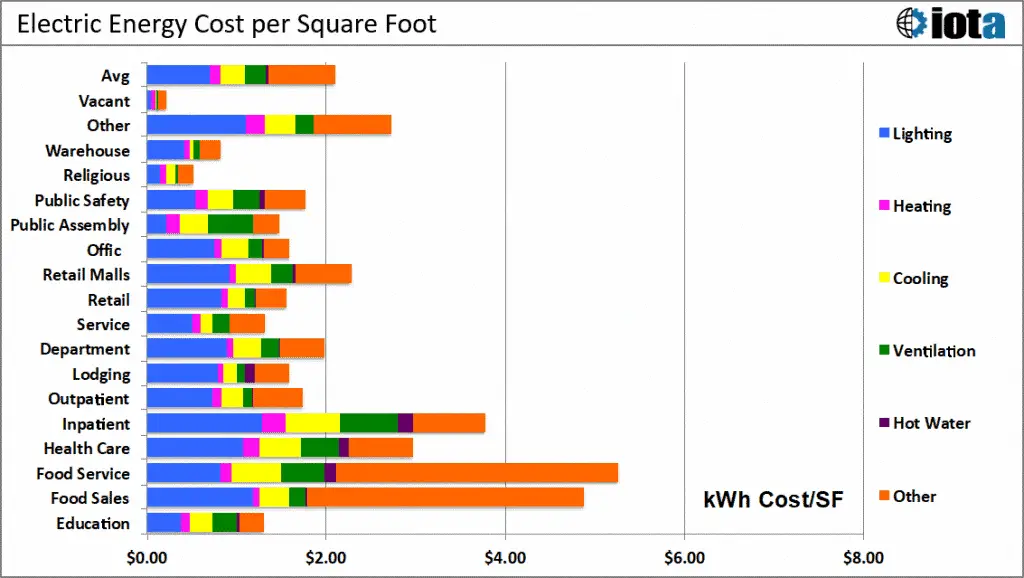
Image credits: Iota Communications
Factors that affect this cost range
Commercial electrical costs are driven by factors like building size and requirements for high-tech amenities. The costs typically include installations for outlets and switches alone, so they do not cover fixture or appliance installation costs. If your commercial space requires specific cable types, then this can add to the overall costs as well. Some of the main cost-influencing factors for commercial electrical systems are discussed below.
Labor
You need to hire experienced and licensed electricians who have the relevant expertise for commercial wiring, which should also be strictly code compliant. Generally, commercial electricians charge between $50 – $100 per hour based on the complexity of the project – such as the number of floors and unpredictable configurations. For example, if your existing infrastructure cannot be drilled through, the electricians will have to change the wiring layout accordingly – and this adds to the final cost.
Permits and inspections
Commercial electrical costs per square foot are also driven by permit charges, as all the wiring setups need to meet various building codes to ensure safety and business compatibility. Whether you are constructing a new building or renovating an existing one, your commercial contractor will first tackle permits and approvals so that every project stage – including the electrical framework – stays within the local codes. Once the electrical wiring is in place, your team will also conduct inspections to check the reliability and efficiency of the whole system. Together, permits and inspections can cost between $300 – $700 depending on your project’s specifications.
Project type
New construction projects allow more flexibility in configuring your desired electrical framework, as you can choose the materials and cables from scratch. Renovation projects, on the other hand, might require demolitions to first tear down old and damaged utilities before rewiring everything. Therefore, there is a whole new range of building permits to handle before any electrical work begins. Outdated connections can severely impact the everyday flow of your business, considering how every aspect is tied to electricity. So, fixing any damaged wiring is absolutely crucial, otherwise, you will most likely meet expensive network upgrades down the road.
We mentioned under the labor factor that infrastructural complexities drive up labor charges because electricians charge more per hour for difficult work. This also applies to the installation process itself, so drop ceilings, HVAC systems, spatial upgrades, etc. can all affect your initial budget.
Ways to boost your commercial electrical savings
Businesses often choose to be more energy efficient by implementing various strategies. This could be either from the beginning of the installation process or later on as part of the energy consumption cycle. You can install energy-saving light bulbs, use solar panels, or invest in automation technologies. Smart systems allow businesses to integrate their utilities with sensors and remote app monitoring, which gives them better insights into energy statistics like monthly consumption and wastage.
Energy tracking in this way can help you analyze data patterns to understand which of your commercial fixtures or equipment work the most during peak hours. As a result, you can manage such units more efficiently by setting operation schedules on the app for easier tracking. Maintaining and supervising your commercial building’s energy profile is the best way to make sure that your electrical units last longer and perform better – and keep your carbon footprint under control!
Conclusion
While setting your budget for commercial electrical costs per square foot, remember to leave some room to accommodate unexpected financial challenges up ahead. These challenges could take the form of hefty permits, labor shortage, building incompatibility, and last-minute demolitions. It is always recommended to choose licensed electricians who specialize in commercial projects, as they have exactly the right skills to meet custom specifications. This is also important because professional teams are equipped to oversee everything from permits to final inspections. So, you can rely on them in terms of code compliance and transparency. Poorly installed electrical connections can put your employees and building at a huge risk, which in turn leads to potentially fatal legal setbacks as a business – and that is something no smart owner should gamble with!
FAQ
What Is The Sq Ft Price For Electrical Wiring?
Commercial electrical wiring costs between $2 to $12 per square foot on average. The actual price depends on factors like the type of electrical features needed (such as lighting and HVAC), applicable permits, inspections, and skilled labor for complex projects. On the other hand, electrical wiring for new homes will cost $3 to $7 per square foot, whereas rewiring costs range between $6 to $12 per square foot. Commercial buildings usually have higher square-foot costs compared to residential buildings because they use more technical and heavy-duty applications for the same square footage.
Residential electrical wiring prices are influenced by the size of the home, the age of the home, the total number of outlets and switches, and ease of access to the target places. Since older homes have outdated infrastructures and layouts, they are more expensive to rewire compared to new construction. This is because most of the existing structures need to be updated to ensure compatibility with the new wiring – which makes the installation more labor-intensive per square foot for residential buildings.
How Much Does It Cost To Wire A 3000 Square Foot House?
You can expect to pay around $3 to $5 per square foot to wire up a 3000-square-foot house for the first time, which gives a total of $9,000 to $15,000. This cost is inclusive of all labor, material, and installation charges for key features like panels, wires, switches, outlets, drywall finishes, and so on. Smart home integrations can cost you a few dollars more per square foot, especially if they require extra permits to meet and inspections to pass. For rewiring a 3000-square-foot house, your estimate will be a lot bigger considering the amount of prep work that goes into the project. This creates an average range of $6 to $10 per square foot depending on how labor-intensive the process will be, giving a total of $18,000 to $30,000. For example, a house with basic and straightforward rewiring specifications will cost on the lower end, whereas one that requires opening up a wall will cost on the higher end of this range.
How do you calculate electrical labor costs?
To calculate your electrical labor cost during the bidding stage, you need to:
1. Review your project’s electrical specifications on the request for proposal (RFP) document to understand the scope of work ahead. This will help you set relevant prices based on what the project needs.
2. Analyze construction drawings and blueprints to zoom in on your project’s electrical requirements.
3. Conduct a material takeoff to finalize your electrical inventory and associated costs. This will help you find out relevant counts for all the electrical features to be installed – such as circuits, switches, outlets, wires, light fixtures, conduits, etc.
4. Calculate your electrical labor cost based on the above information by estimating the number of hours needed to complete the work, finding out how many electricians are required, factoring in project complexities, considering automation needs, and so on. In general, commercial electricians charge between $50 to $100 per hour depending on the type of project involved. Apprentices may charge around $50 per hour on average, whereas journeyman electricians charge around $75 per hour, and master electrician rates can go up to $120 per hour.
You can use the following formula to get your final estimate:
- [Hourly labor rate] x [Number of hours] = Electrical labor cost
You can also charge a flat fee instead of hourly rates, though most electricians prefer charging per hour.
5. Add your operational costs to account for various overheads like fuel, taxes, and equipment in the final estimate, and then figure out a good markup before finalizing your total electrical labor costs to go into the bid.
How do you calculate electrical construction?
Electrical construction costs are calculated based on the project’s electrical specifications and material takeoffs, as they form the main starting point in estimating the number of hours needed, the associated costs for electrical parts, as well as the number of electricians to hire. If the project includes labor-intensive aspects like smart home integration or full-scale rewiring, this is your chance to incorporate all those heavy costs into the estimate. Make sure to also leave some room to accommodate reworks in case of construction setbacks, permit issues, inspection results, and so on. Otherwise, you will end up underpricing your electrical work and not have enough budget to confront unexpected changes down the road. Once you determine the total hours for the work, you can multiply your hourly rate by the total hours to get your total electrical labor costs. You can then factor in applicable overhead costs to complete the estimate before submitting your quote.
How much does it cost to rewire a 2000 sq ft house?
It takes around $2 to $4 per square foot to rewire a 2000-square-foot house, so that gives a total of $4,000 to $8,000 for a complete rewiring project. Older homes are more expensive to rewire compared to new homes, especially because their outdated and incompatible electrical materials are not equipped for modern technologies. In addition, older buildings can increase the level of difficulty to access the target areas and call for more demolitions before any installation takes place – all of which require additional permits and inspections, making it quite expensive to rewire the space. So, you can expect to add a dollar to each end of the range if you are rewiring an old 2000-square-foot house and need to add the necessary retrofits to make the space more compatible with your electrical systems.
How much does it cost to run a 220 line for a dryer?
The general range to install a 220V line for a dryer is from $135 to $300. Though the average cost is around $250 for most homes, various project complexities can increase the costs to $500 and even reach $1,000 and above for large-scale installations. For example, factors like circuit length, ease of access, labor charges, and retrofit aspects can cost you more to wire up and install your dryer. You need the wire to run from the electrical panel to where your dryer is located, so depending on the circuit length as well as ease of access to the desired place, you can expect higher labor rates if there is more work involved – like when the wire runs multiple floors up to connect to the dryer.
